


It may be noted that one contour is located at a time. The line joining all these points gives the required contour. Similarly various other points are marked on each contour. The staff is held on an approximate position of point and then moved up or down the slope until the desired reading is obtained. As an example, if the height of instrument is 72.58 m, then the staff readings required to locate the 72, 71 and 70m contours are 0.58, 1.58 and 2.58 m respectively. The staff readings required to fix points on the various contours from the height of instrument. and adding it to the R.L of the bench mark. The height of instrument is determined by taking a back sight on the B.M. The level is then set up in such a position so that the maximum number of points can be commanded from the instrument station. is established near the area to be surveyed with reference to a permanent B.M. This is suitable for small areas and where great accuracy is required. This method is the most accurate but very slow and tedious as a lot of time is wasted in searching points of the same elevation for a contour. These points are then surveyed and plotted on plan and the contours drawn through them. In this method, the contours to be located are directly traced out in the field by locating and making a number of points on each contour. There are mainly two methods of locating contours Line passing through the saddles and summits gives water shed line. And in the case of a mountain range, it takes the form of a pass. It represents a dip in a ridge or the junction of two ridges. It is represented by four sets of contours as shown in Fig. Depression between summits is called a saddle. In this case, several contours coincide and the horizontal equivalent becomes zero.ġ0. Contours never run into one another except in the case of a vertical cliff (Fig. Contour lines cannot merge or cross one another on map except in the case of an overhanging cliff. Contour lines cannot end anywhere but close on themselves elders within or outside the limits of the map.Ĩ. 8.3).Īnd if the higher values are outside the bend, it represents a “Valley” (Fig. If the higher values are inside the bend or loop in the contour, it indicates a “Ridge”. Contour lines across ridge or valley lines at right angles.
#Height of contour definition series
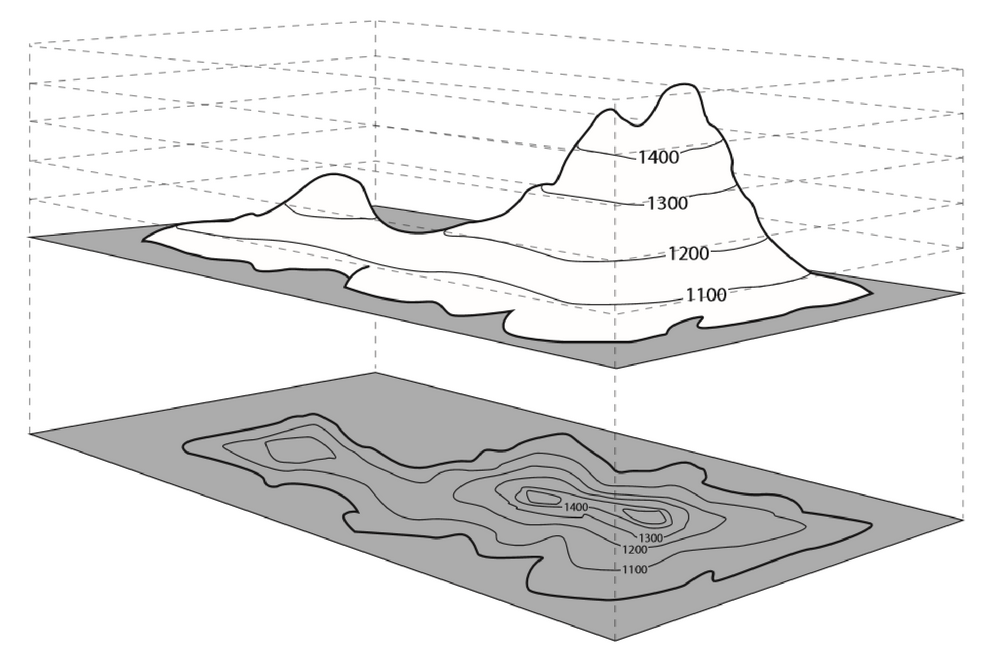
A series of closed contours on the map indicate a depression, if the higher values are outside (Fig. A series of closed contour lines on the map represent a hill, if the higher values are inside (Fig. A uniform slope is indicated when the contour lines are uniformly spaced and a plane surface when they are straight, parallel and equally spaced.Ĥ. Flat ground is indicated where the contour are widely separated and the steep ground where they run close together.ģ. Contour Interval and Horizontal Equivalent:Ģ. Thus a contour map serves the purpose of both, a plan and a section. A contour map therefore, gives an ides of the altitudes of the surface feature as well as their relative positions in plan. The process of tracing contour lines on the surface of the earth is called contouring and the maps upon which these lines are drawn are called contour maps. And if the level of water is raised successively by 1 m, the successive shorelines represent 61, 62, 63 m contours and so on. Supposing a depression is partly filled with water and R.L of the water surface is say 60 m, then the shore line of this water represents 60 m contour. This means every point on a contour line has the same altitude as that of the assumed intersecting surface. Definition of Contour:Ī contour or a contour line may be defined as the line of intersection of a level surface with the surface of ground. Contour Interval and Horizontal Equivalent 3. After reading this article you will learn about:- 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
